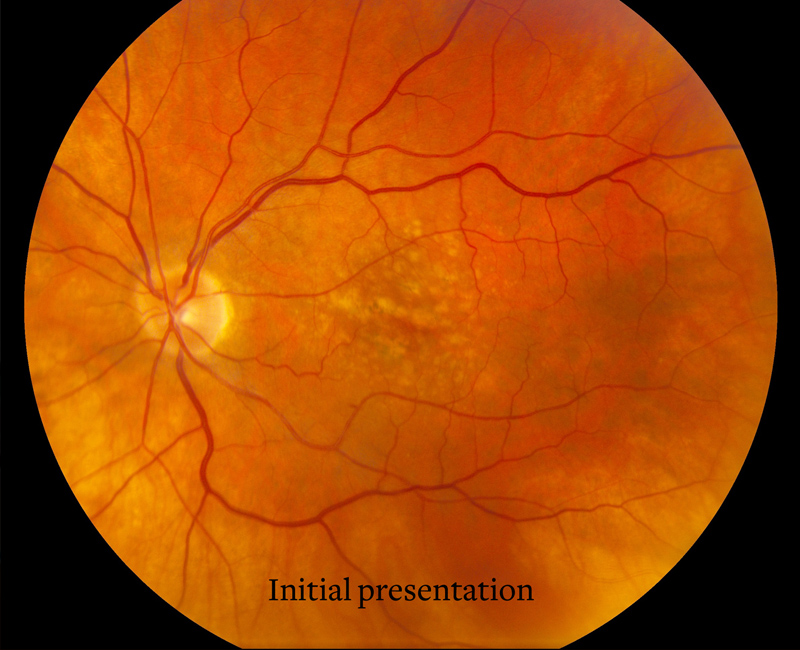
Overview
Diabetic retinopathies refer to any damage that occurs in the eyes’ retina in connection with long term diabetes. (Retinopathies refer to non inflammatory diseases of the retina) Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness among American adults.
Warning Signs & Symptoms
Early diabetic retinopathies have no symptoms, but as they progress, symptoms include:
- blurred vision
- blindness
- floaters
- missing areas of vision
There are two stages of diabetics retinopathy:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retina, in which blood vessels leak. If the leakage causes fluid accumulation in the retina, bluring of vision occurs.
- The later stage, proliferation of diabetic retinopathy, happens when the blood vessels in your eyes close and abnormal ones grow instead. This can cause blindness, as well as detachment and glaucoma of the retina.

Treatment
Treatment doesn’t cure damage, but it can help prevent further problems. Lasers can shrink abnormal blood vessels, and surgery can remove the vitreous fluid from the eye. Vitrectomies can stop bleeding in the eye.
Prevention Since early stages can be asymptomatic, every person with diabetes should have an eye exam annually. Some groups are at greater risk because they are likely to have diabetes: African American Latinos Native Americans
People at high risk should closely track blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol.

